Why Condensation Can Occur at Any Time in the Greenhouse
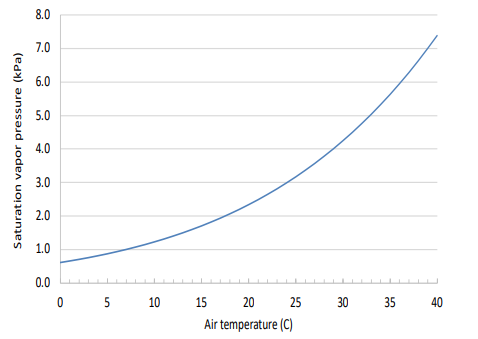
Saturation vapor pressure (kPa) or the maximum amount of moisture that air can hold at different air temperatures. Saturation level of humidity (vapor pressure) generally doubles every 10 degrees Celsius (18 degrees F).
When moist air meets a surface having a temperature lower than its dewpoint, oversaturated humidity in the thin layer of air touching the surface turns into liquid water (dew, or condensate). This rather simple phenomenon is often overlooked and misunderstood. A typical misunderstanding is that condensation happens only when the greenhouse air is saturated or nearly saturated (i.e. 100% relative humidity). This is not true, and condensation can happen inside a greenhouse whose air humidity is not yet saturated. In fact, condensation does not happen even when the air humidity is 100% if the surfaces are all higher temperature than the air (i.e. dewpoint).
A recent article on E-GRO.org from Dr. Chieri Kubota, professor in the Department of Horticulture and Crop Science at The Ohio State University and Director of Ohio Controlled Environment Agriculture Center, aims to assist growers in understanding some of the critical psychrometric properties, saturation humidity (or saturation vapor pressure) and dewpoint. Understanding them would help growers avoid creating the conditions causing unnecessary condensation dripping onto or forming on crops.
Warmer air can hold more moisture (humidity). Saturation level of humidity doubles every 18 degrees F. When air cools down, the capacity to hold moisture (humidity) is lowered, shown as lower saturation levels. When air temperature decreases further to the level where the air no longer can hold the humidity, excessive humidity becomes small droplets of liquid water or dew (or fog when floating in the air). This process, turning humidity (vapor) into liquid water, is called condensation and the temperature at which condensation occurs is called dewpoint. Air at the dewpoint temperature has 100% relative humidity. When greenhouse has a localized low temperature area (e.g., near cold surface) dew forms on such a cold surface due to condensation.
To learn more, including three cases that help better understand condensation risk management in crop production, check out the original e-GRO alert here.










